Your Apps Are Listening: 10 Ways Technology Collects Personal Data & 10 Ways to Protect Yourself
Your Apps Are Listening: 10 Ways Technology Collects Personal Data & 10 Ways to Protect Yourself
It’s a Technology-Ridden World—You're Right to Be Paranoid
Think about what sites you've visited today, how many pages your browsing history is riddled with. How many clicks did it take to get you to this article? In what ways have you interacted with your other devices? If this heightens your paranoia, don't worry—it should. Here are 10 ways technology is collecting your personal data and 10 ways you can protect yourself.
1. Website Cookies
Every time you click on a website, you're often greeted with a message: "This site uses cookies to improve your browsing experience." More often than not, you probably click "accept" just to get the window out of the way. But by allowing sites to use cookies (small blocks of data sent to your browser), you're allowing them to track your logins, activities, shopping carts, and preferences. This is why you might see similar items pop up right after you've viewed something.
 Einladung_zum_Essen on Pixabay
Einladung_zum_Essen on Pixabay
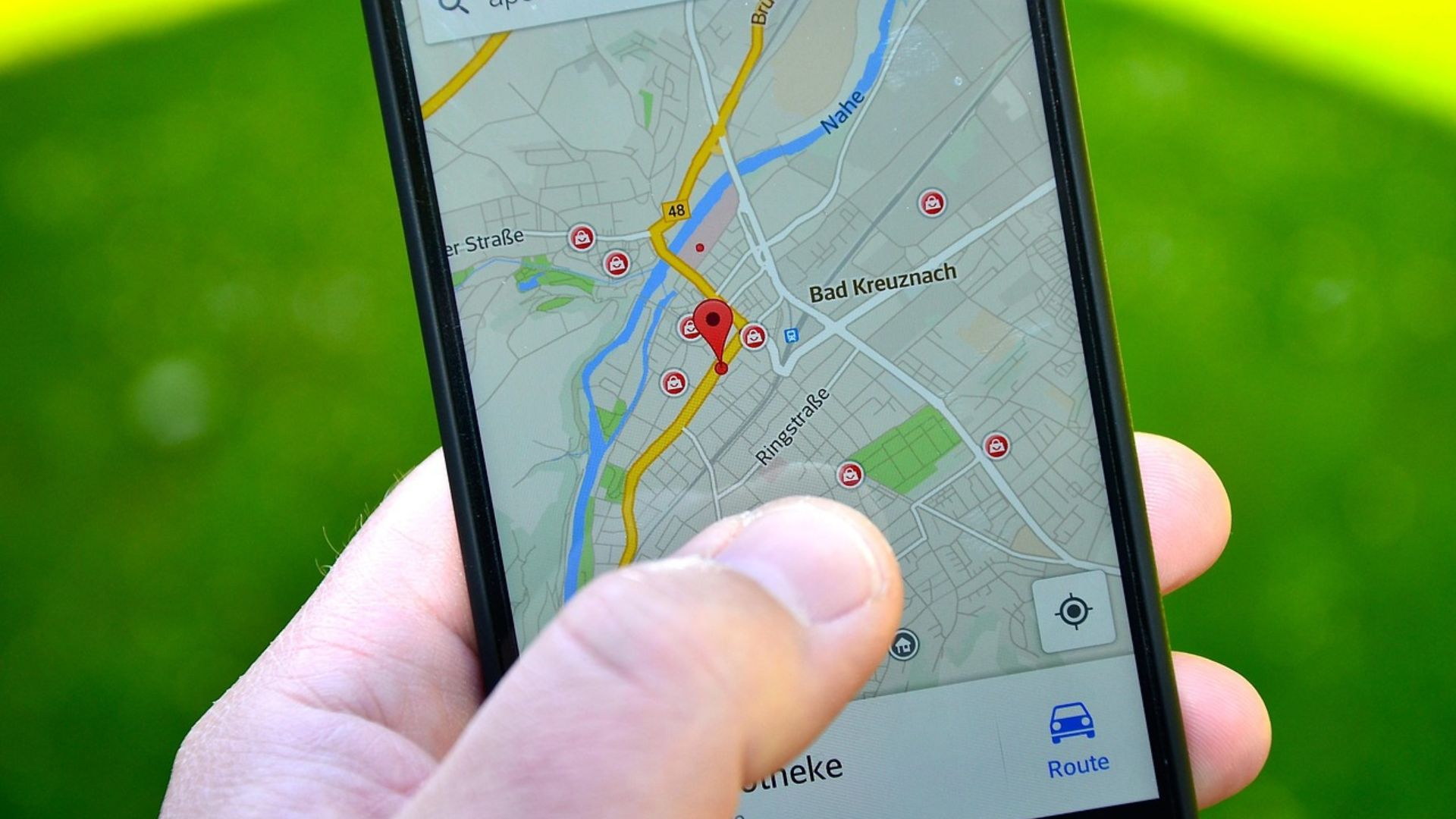
2. Location Tracking
In order to use certain apps and websites, you may sometimes need to share your location. This allows the provider to see where you are and match you to better, more relevant searches or information. But by keeping this option turned on, you permit these apps to always know where you are.
3. Social Media Interactions
The posts you like, comment on, view, and interact with on social media are also being monitored by the apps and platforms you use. Even data from your private conversations, what posts you click on, what videos you watch—all this information is collected to personalize your experience, refine the algorithm, and tailor advertisements to your liking.
4. Biometrics
Gone are the days of fingerprint recognition, which, in hindsight, seems to be less invasive than collecting your facial biometrics. But the latter is what's on the rise, and as easy as it is to have your face be the password to various apps, this system has sparked concerns about how your private information is collected, stored, and used. After all, what if there were a data leak?
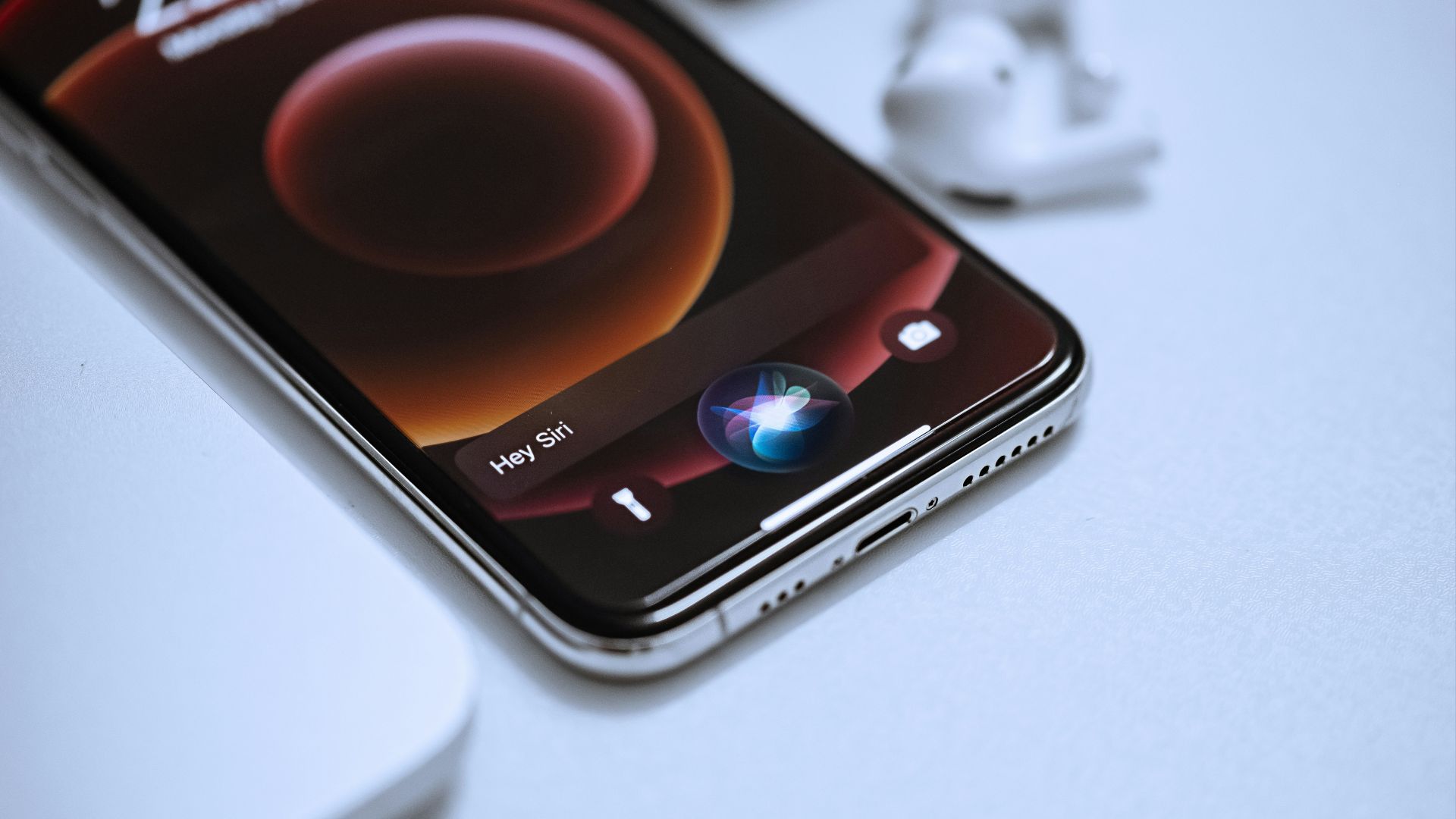
5. Voice Assistants
Voice assistants, like Siri and Alexa, are always listening. They're designed to stay alert, waiting for the wake command (such as "Hey Siri"). Once they're activated, they collect information like speech patterns, your specific question, your voice, and sometimes your location. Specific tasks may also mean they'll access your calendar, contacts, and emails.
6. Smart Devices
Other smart devices, like your TV or speakers, are also listening. In fact, anything that waits for a specific command, whether it's a wake command or a certain prompt, will mean that the device is always ready and alert to react to your voice. Depending on the device, they may also collect video data alongside audio.
7. App Permissions
Your apps need certain permissions enabled to work. Sometimes, this means they'll need to access your GPS location, photo library, microphone, contacts, calendar, and more. Every time you permit apps to access your information, you allow them to view, scan, and collect your private data.
8. Wi-Fi & ISP Monitoring
Your ISP (internet service provider, or the company that provides you to access the web) can also see your browsing history and the sites you visit. Unless you use a VPN (virtual private network) which protects your data by encrypting it and hiding your IP address (a unique number assigned to your device and is linked to your online identity), you risk your web traffic—including your search inquiries—being seen.
9. Payment Data
Every time you make a transaction, whether online or in person, personal data is collected. While your credit card information is encrypted to allow secure payments, data breaches can still happen. Plus, your shopping patterns and the things you purchase are then used to personalize the ads and items you see.
10. Wearable Devices
Wearable technology, like fitness trackers and smartwatches, also raises security and privacy concerns. While they're helpful for collecting health and behavioral patterns, this information can be accessed by third parties who may take your data from the cloud servers it's synced to and use them for various purposes—such as being sold to advertisers—without your knowledge or consent.
But with technology playing such a big part in our daily lives, it's inevitable that our data will be collected. The next important step, then, is knowing how to protect yourself. How? Let's explore 10 ways.
1. Reject Cookies
Whenever you click on a website and a notice pops up about cookies, reject it. The option is usually there, even if it's less accessible or obvious than the "accept" button. You can also configure the settings to only allow necessary cookies.
2. Log Out of Shared Accounts & Devices
If you share any computers, phones, or accounts with anyone else, even if it's your family member, make it a habit to log out whenever you're finished using it. Never sign in to these accounts on public devices, especially if they contain private information.
3. Be Careful What You Click On
If you've accepted cookies or app permissions, you're probably familiar with how your data is tracked and monitored. Whenever you click on something, the algorithm tries to further personalize the content you see. But other times it can have a more adverse effect, such as when you click on ads and potentially malicious links, which could compromise your private data.
4. Use End-to-End Encryption
When using messaging apps, use ones with end-to-end encryption, like iMessage or WhatsApp. This means your texts will be kept as essentially gibberish blocks of data until it reaches the recipient, which prevents third parties from accessing and reading your messages.
5. Limit Social Media Use or Keep It Private
Your digital footprint also matters when keeping your private data safe. Uploading photos, posts, videos, and more—especially with personal information attached like locations and birthdays—can make it all the more easier for cyber criminals to note these details down and exploit you. While social media allows you to stay connected with your loved ones, limit your use—or private your account.
6. Use Secure Wi-Fi Connections
Public Wi-Fi is often unsecured, meaning anyone could potentially hop on the network, snoop at your browsing activity, and steal your data. Never log into accounts with sensitive information or make payments when connected to an unsecured network.
7. Pay Attention to App Permissions
When downloading a new app, pay attention to what's needed for it to run on your device. They may need to access your camera, photos, microphone, location, and activity, depending on the purpose of the app. If you mindlessly accept all permissions, you're allowing your personal data to be viewed and accessed at all times.
8. Use Secure Passwords
This should go without saying, but make sure your passwords are unique across all accounts and that they don't contain sensitive information. If you always reuse the same password or include important numbers and names—like your birthday or full name—you risk someone hacking into your system and stealing your data.
9. Be Wary Where You Share Personal Information
Before entering sensitive information like your full name, date of birth, home address, and credit card information, ensure that the platform you're on is secure and can be trusted. You should also avoid making too many accounts on the same site where personal data is collected, since, if you forget you had that account, someone could eventually hack into it and steal your information.
10. Keep Software Up to Date
Software updates typically include security patches and bug fixes, which allow your system to run smoothly and keep your data protected. If you're always skipping these downloads, you could be putting yourself and your devices at risk.